Population: 83,888 million inhabitants – Administrative language: german
Political capital: Berlin
Political system: Germany is a federal parliamentary republic headed by a head of government, the Chancellor, and a head of state, the President, who essentially performs a representative function. The country is made up of 16 states, each with its own constitution and a high degree of autonomy over its internal organisation. 3 of them are city-states: Bremen, Hamburg and Berlin.
A member of the European Union (1958), the Schengen area (1995) and the euro zone (1999).
Brief rail characteristics:
• UIC code : 80
• Main track gauge: 1,435mm
• Main electrification: 15kV
• High Speed > V250 : yes
Rail transport
• History of rail in Germany
• Details of institutional organisation
• German’s rail news highlights
Notified bodies
• Regulation : Bundesnetzagentur
• Security : Eisenbahn – Bundesamt (EBA)
Public transport
• National / local and regional authorities
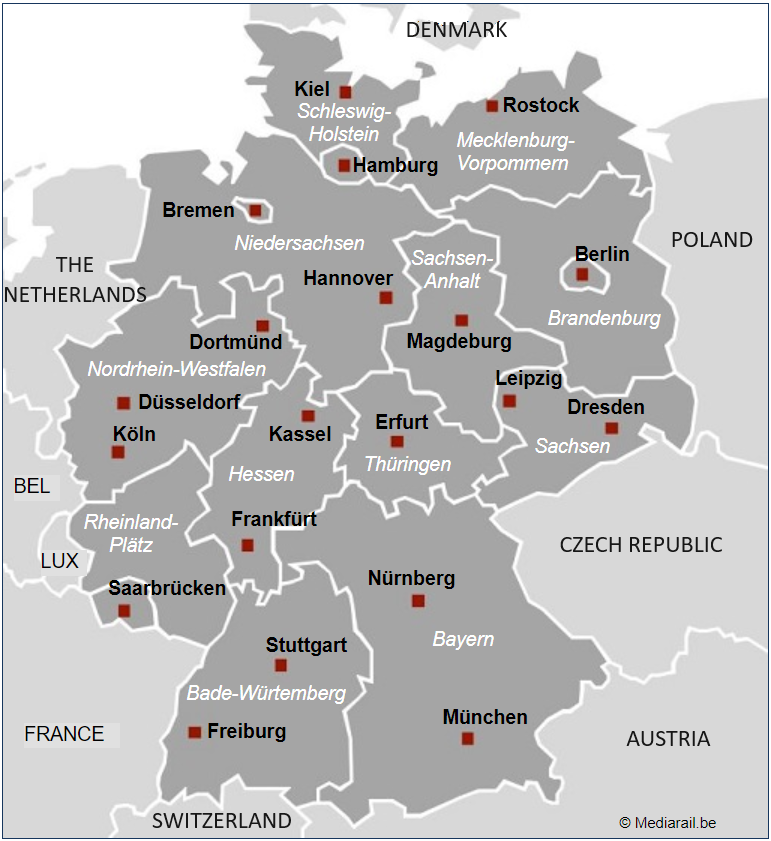
The 10 top ranking cities:
• Berlin, Hambourg, Munich, Cologne, Francfort, Stuttgart, Düsseldorf, Leipzig, Dortmund, Essen
Organisation of rail transport in Germany
Manager of the main railway network
DB InfraGO AG, subsidiary of DBAG Holding
Main historical railway company
Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB) since 1949, renamed DBAG in 1994
Public limited company – Holding company with subsidiaries
Liberalisation (depends on the legal scope given to it)
International passenger traffic: yes
National mainline passenger traffic: yes
National regional and local passenger traffic: DB Regio + various operators
Freight: numerous independent operators
Mainline and international train services
Non-subsidised mainline trains: classic Intercity and high-speed ICE in a non-subsidised framework.
ICE/TGV traffic to Paris managed in cooperation with SNCF (France) under the name Alleo.
ICE traffic to Brussels and Amsterdam, managed under a service contract with SNCB (Belgium) and NS (the Netherlands).
Nightjet traffic managed under service contract with ÖBB (Austria).
Alternative mainline operators
Flixtrain, Snälltåget, WESTbahn, SJ
Local / regional train services
Subsidised regional and local trains:
The Länder operate their regional and local trains under contract and invitation to tender, within a subsidised framework, with total choice of operator.
Other local and regional operators
A large number of operators, accounting for a good third of regional and local traffic in Germany.
Freight train services
• DB Cargo AG is an independent company. It was first called Railion from 2000 to 2009, and then became DB Schenker Rail. In 2016, it changed its name to DB Cargo.
• DB Cargo has numerous subsidiaries abroad under various names, including ECR in France and DB Cargo Belgium in Belgium.
Alternative rail freight operators
Numerous private rail freight operators
Bus / lightrail / metro
The regions are responsible for programming, planning and supervising their public transport, as are the major cities.
Glossary of rail transport in Germany

Infrastructure
◼ Main network manager:
• DB InfraGO AG
• 38,466km of lines
◼ Others secondary network managers:
• —
◼ High speed lines
◼ Passenger stations :
• 5,381 (InfraGo)
◼ Companies registered:
• 630
◼ Main issues:
• S-Bahn
• Deutschland Takt
• Signalling & ETCS

Rolling stock:
◼ Authorized vehicles:
• Electric vehicles
• Autonomous vehicles
• Emu
• Dmu
• Railway cars
• Freight wagons
• Others
◼ Suppliers:
• History of the industry
• Industry today

Passenger services:
◼ Incumbent:
• DBAG
• National traffic yesterday
• Intercity concept
• Transports today
• S-Bahn networks
• Cross-border traffic
◼ international trafic :
• Traffic organisation
◼ Stations:
• 5,381
• History & Heritage
◼ Flow analysis:
• Main lines / local lines
• Modal shares & Economy

Freight services
◼ Industry sectors:
• Steel
• Chemical
• Intermodal
• Wood / Paper
• Others
◼ Operators:
• DB Cargo
• Others
◼ German’s operations abroad:
• DB Cargo subsidiaries
• Metrans (HHLA)
◼ Infrastructure :
• little freight stations
• Marshalling yards
• Main north-south routes
• Ports
◼ Flow analysis:
• Main freight lines
• Modal share & Economy