Population: 11,912 millions inhabitants – Three national languages: french, dutch, german
Political capital: Brussels
Political system: Belgium is a federal constitutional monarchy ruled by a head of state, the King, and a head of government, the Prime Minister, in a multi-party system. Decision-making power is not centralized, but divided between 3 levels of government: the federal government, 3 linguistic communities (Flemish, French and German-speaking) and 3 regions (Flanders, Wallonia and Brussels-Capital). Legally, they are all equal, but their powers and competences cover different areas. Along with Luxembourg and Strasbourg, Brussels is one of the three official seats of the European institutions.
Member of European Union (1958), the Schengen area (1995) and the euro zone (1999)
Caractéristiques ferroviaires succintes
• UIC code : 88
• Main track gauge : 1435mm
• Main electrification : 3kV DC, 25kV AC
• High Speed > V250 : yes
Rail transport
• Railway history in Belgium
• Details of institutional organisation
• Belgian rail news highlights
Notified bodies
• Regulation : Regul.be
• Security : NSA Rail Belgium
Public transport
• regional authorities
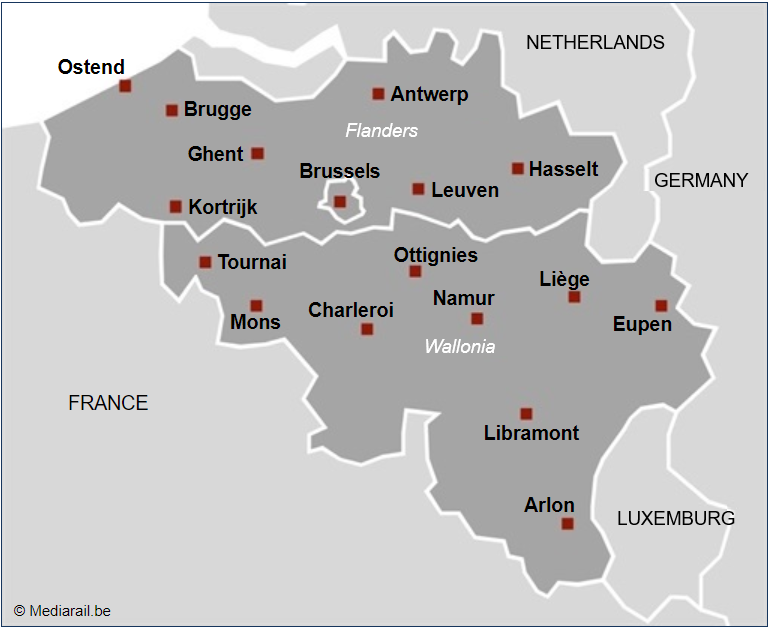
The 10 top ranking cities:
• Brussels (19 municipalities), Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Brugge, Namur, Leuven, Mons, Aalst
Organisation of rail transport in Belgium
Manager of the main railway network
Infrabel, as independant company since 2005.
Main historical railway company
Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer belges (SNCB) since July 1926
Dutch name: Nationale Maatschappij der Belgische Spoorwegen (NMBS)
Public limited company since March 1991 – Group with several subsidiaries
Liberalisation (depends on the legal scope given to it)
International passenger traffic: TGV Eurostar considered as independent RU, ICE (DB), Nightjet in cooperation, European Sleeper (private), cross-border traffic operated by SNCB / NMBS.
National mainline passenger traffic: considered international
National regional and local passenger traffic: not liberalized
Freight traffic: fully privatized since 2017 – Lineas dominant (ex B-Cargo) – several other operators
Mainline and international train services
TGV Eurostar and Thalys, in the process of merging, considered as independent RUs
Service contract with ICE, the ‘Benelux’ train (Netherlands), Nightjet ÖBB, etc.
Service contract with TGV Inoui SNCF (to Lille, Lyon, Montpellier, etc.)
Alternative mainline operators
European Sleeper from June 2023 on Brussels-Amsterdam-Berlin-Prague
Local / regional train services
Exclusively national competence – Regions on consultation
Exclusive monopoly of SNCB / NMBS until 2032
Specific contract for local cross-border service (Roosendaal, Maastricht, Aachen, Luxembourg, Maubeuge and Lille)
Other local and regional operators
Dutch operator Arriva NL between Maastricht and Liège since June 2024 (in cooperation with SNCB).
Freight train services
Completely private – several operators, mainly in Antwerp
The former B-cargo became Lineas in April 2017 and is now the dominant fully private operator.
Alternative rail freight operators
Several operators
Bus / lightrail / metro
The Regions are responsible for programming, planning and supervising local public transport:
Walloon Region: SRWT (under the TEC brand)
Flemish Region: De Lijn
Brussels Region: STIB / MIVB
Glossary of rail transport in Belgium

Infrastructure
◼ Main network manager:
• Infrabel
• 3,627km of lines
• 3,222km of electrified lines
• HSL> 250km/h : 202 km
◼ Others secondary network managers:
• Former local railways (SNCV), now De Lijn
◼ Passenger stations :
• 555 (SNCB / NMBS)
◼ Companies registered:
• 14 operators
◼ Main issues:
• Suburban project around Brussels (RER)
• Signalling & ETCS

Rolling stock:
◼ Authorized vehicles:
• Electric vehicles
• Autonomous vehicles
• Emu
• Dmu
• Railway cars
• Freight wagons
• Others
◼ Suppliers:
• History of the industry
• Industry today

Passenger services:
◼ Incumbent:
• SNCB / NMBS
• National traffic yesterday
• Regional traffic
• TGV, Eurostar, ICE
• RER around Brussels
• RER in other cities
• Crossborder traffic
◼ international trafic :
• Traffic organisation
◼ Stations:
• 555 (SNCB / NMBS)
• History & Heritage
◼ Flow analysis:
• Main lines / local lines
• Modal shares & Economy

Freight services
◼ Industry sectors:
• Steel
• Chemical
• Intermodal
• Wood / Paper
• Others
◼ Operators:
• Lineas
• Others
◼ Belgian operations abroad:
• Lineas
◼ Infrastructure :
• little freight stations
• Marshalling yards
• Main north-south routes
• Ports
◼ Flow analysis:
• Main freight lines
• Modal share & Economy